Big Data Exploitation in Life Sciences
Modern life sciences rely on increasingly complex analytical methods that generate large amounts of data to be analysed. This requires extensive knowledge and powerful bioinformatics tools.
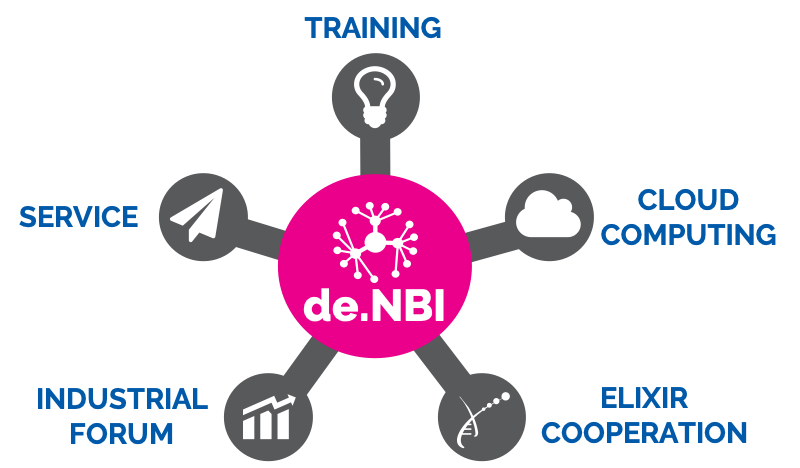
The German Network for Bioinformatics Infrastructure – de.NBI - is the key to solving this challenge.
- to provide cutting-edge bioinformatics tools & services for the life sciences and biomedicine
- to provide high-quality bioinformatics training through a wide spectrum of workshops and courses
- to offer scalable cloud computing resources for academia in Germany
- to foster knowledge exchange between academia and industry through our Industrial Forum
- to strengthen ties between the German bioinformatics community and international bioinformatics networks such as ELIXIR Europe
Since August 2016, the de.NBI has constituted the German node of the ESFRI ELIXIR, ELIXIR Germany. Since 2022, the Forschungszentrum Jülich as a member of the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centers has been entrusted with continuing the de.NBI.
History
In May 2013, the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) published funding guidelines for the de.NBI network to address the "big data" problem in life sciences through bioinformatics services and training.In November 2015, a second call for de.NBI partner projects was announced to amend the range of topics. The de.NBI programme finally launched in March 2015 and the partner projects began their work in November 2016.
Coordinator of the project and Head of the German ELIXIR Node was Alfred Pühler, Bielefeld University (2015-2021).
The BMBF funding was initially granted 2015 to 2021. By decision of the Federal Government from November 2020, the de.NBI will receive a long-term funding from the BMBF for contuation by Forschungszentrum Jülich, a member of the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centers.