Kersten Breuer, Marius Dieckmann, Sven Twardziok, Chris Lawerenz and Pavlo Lutsik
Service centers: Heidelberg Center for Human Bioinformatics and Bielefeld-Gießen Resource Center for Microbial Bioinformatics
Making scientific computing infrastructure accessible to the entire interdisciplinary life science community is a core objective of de.NBI. The COVID-19 pandemic underlined the importance of flexibly satisfying the abruptly changing computational resource needs to enable fast scientific inference. Thereby, three factors are of key importance: (1) data security, (2) ease of use, and (3) reproducibility as well as portability of the analysis. Building a Europe-wide, standardized computational environment that fulfills these constraints is the aim of the ELIXIR Cloud and AAI project1. This is achieved by realizing Cloud-based implementations of the Workflow Execution Service (WES)2 and Task Execution Service (TES)3, which are defined as open standards by the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH). Thereby, the Authentication & Authorization Infrastructure (AAI) surveils each step of the analysis deployment to prevent any potential misuse. While this setup ensures a high degree of portability and scalability, the service interfaces are not readily accessible to people without programming skills. To this end, de.NBI researchers from the German Cancer Research Center (K. Breuer and P. Lutsik), the Justus-Liebig University in Gießen (M. Dieckmann), and the Charité Berlin (S. Twardziok and C. Lawerenz) contributed an open-source web framework, that combines the underlying services into a user-friendly graphical interface CWLab4. The technical details of a typical usage scenario are summarized in Figure 1. During the ELIXIR All-Hands meeting on June 10th, the researchers demonstrated the simplicity of the web application during a hands-on session. Using public resources from NCBI Virus5, the participants were comparing the sequences of COVID-19 surface glycoprotein from patients in China sampled in 2019 with a cohort sampled during the initial pandemic wave arriving in Europe in 2020. To view the results, interested readers are welcome to repeat the analysis by following the step by step guide at https://tinyurl.com/yc5duq46. The project’s future focus will be to enable collaboration on sensitive clinical data so that patient cohorts from different institutions can be effectively combined and analyzed together without the need to share the restricted raw data.
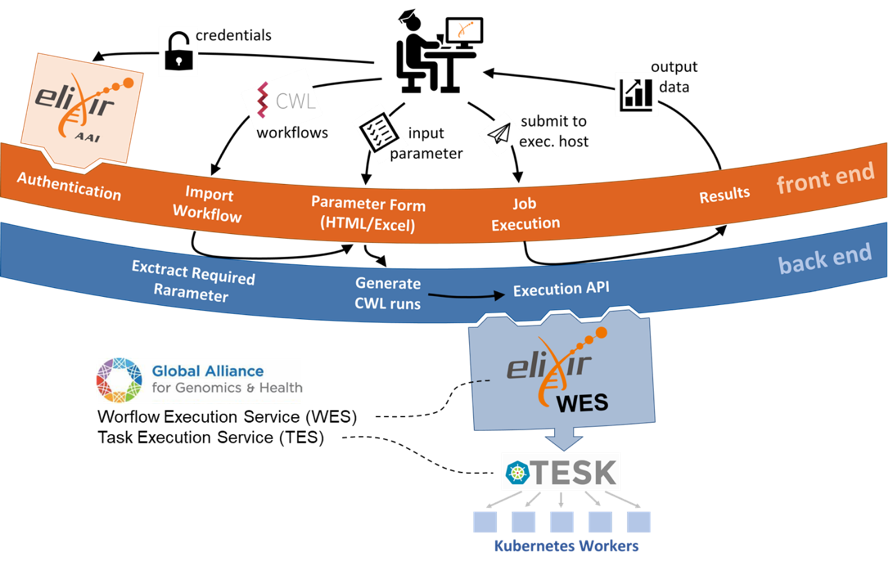
Figure 1. Schematic overview of a typical usage scenario. In brief, the user logs into the web portal via ELIXIR AAI. Any analysis workflow defined in the Common Workflow Language (CWL)6 can be imported and user-friendly HTML form of required workflow parameters will be automatically generated. The user-defined job can be submitted to a WES endpoint of choice. The Task level execution is handled by the TES implementation for Kubernetes (TESK).
Links and references:
- ELIXIR Cloud and AAI project, https://github.com/elixir-cloud-aai/elixir-cloud-aai
- GA4GH WES: https://github.com/ga4gh/workflow-execution-service-schemas
- GA4GH TES: https://github.com/ga4gh/task-execution-schemas
- CWLab: https://github.com/CompEpigen/CWLab
- NCBI Virus: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/labs/virus/vssi/#/
- The Common Workflow Language (CWL): https://www.commonwl.org/